All News
Honorary doctorate for Eberhard Grün
The Max Planck Institute for Nuclear Physics congratulates Prof. Dr. Eberhard Grün on being awarded an honorary doctorate by the University of…
News about the methylidine ion’s chemistry in interstellar clouds
Measurements under space conditions at the ultracold storage ring CSR of the MPI for Nuclear Physics for the first time provided reliable data on the…
Electrons and photons in a twin pack
Resonant two-photon ionisation of helium measured with angular resolution
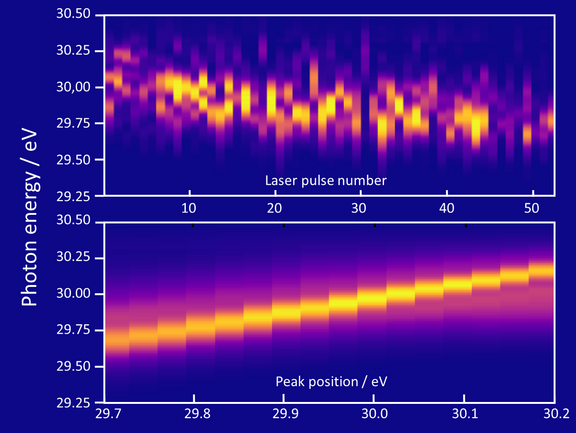
World's first optical atomic clock with highly charged ions
Optical atomic clocks are the most accurate measuring instruments ever built and are becoming key tools for basic and applied research, for example to…
20 years H.E.S.S. telescopes in Namibia
With a ceremony on 18 October and an open day the following Sunday, the H.E.S.S. collaboration celebrated the 20th anniversary of the commissioning of…
José R. Crespo López-Urrutia Fellow of the American Physical Society
“For groundbreaking experiments on sympathetic cooling of highly charged ions and many contributions to spectroscopy for astrophysics, plasma physics,…
Trauer um Volker Soergel
Das Max-Planck-Institut für Kernphysik trauert um sein Auswärtiges Wissenschaftliches Mitglied Prof. Dr. Dr. h.c. mult. Volker Soergel, der im Alter…
Erfolgreiche Feinmechanik-Azubis
Ein komplettes Lehrjahr konnte seine Ausbildung zum Feinwerkmechaniker, Fachrichtung Feinmechanik ein halbes Jahr früher als üblich abschließen. Alle…
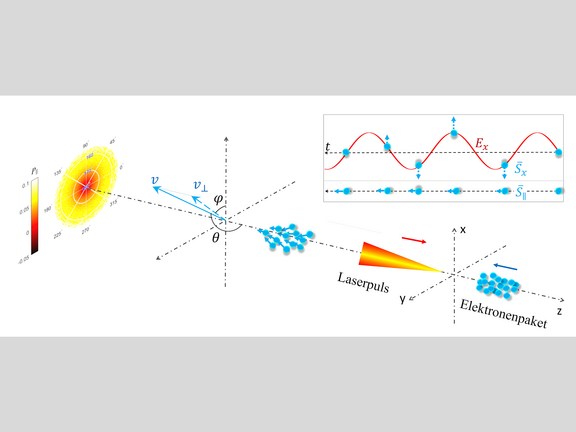
Suitable polarization of ultrarelativistic electrons for high-energy experiments
High-precision high-energy physics at accelerators demands longitudinally spin-polarized electron beams, e.g., the Q-weak experiment at Jefferson Lab…
Klaus Blaum elected to the Heidelberger Akademie der Wissenschaften
Since 06.09.2022 Klaus Blaum is officially a full member of the Heidelberger Akademie der Wissenschaften. As director at the MPI for Nuclear Physics,…
A second Higgs can enable light Dark Matter particles
There must be much more matter in the Universe than is visible. The nature of this dark matter is still a big puzzle − despite numerous attempts to…
Westerlund 1: a powerful cosmic-ray accelerator
Since more than 100 years, we know that cosmic rays – charged particles – are accelerated to extremely high energies in the Milky Way, our galaxy. And…
First results from a Search for New Physics in Electronic Recoils from XENONnT
XENONnT, the latest detector of the XENON Dark Matter program, shows an unprecedentedly low background which facilitates searches for new, very rare…
Statistics from Outer Space - The MPIK at the Explore Science
What do two dice have to do with the acceleration of charged particles in the universe? How do researchers detect extremely energetic light from…
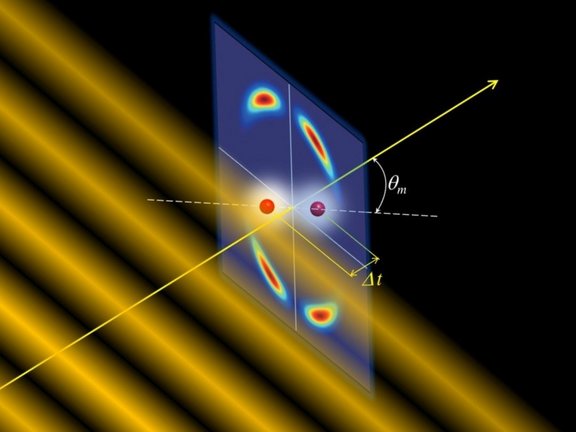
Molecular double-slit and quantum tunnelling in intense laser light
When a light wave hits a double-slit, a characteristic pattern of bright and dark stripes appears behind the obstacle, generated by constructive or…
Quantum electrodynamics tested 100 times more accurately
Using a newly developed technique, scientists at the Max Planck Institute for Nuclear Physics (MPIK) in Heidelberg have measured the very small…
How magnetic is helium-3?
In a joint experimental-theoretical study, physicists at the Heidelberg Max Planck Institute for Nuclear Physics (MPIK), together with collaborators…
Key milestone towards establishing the CTA Observatory
Formal request to establish the CTAO ERIC submitted
Collisions with electrons cool molecular ions
Laser spectroscopic measurements on methylidene ions in the CSR using the elektron cooler
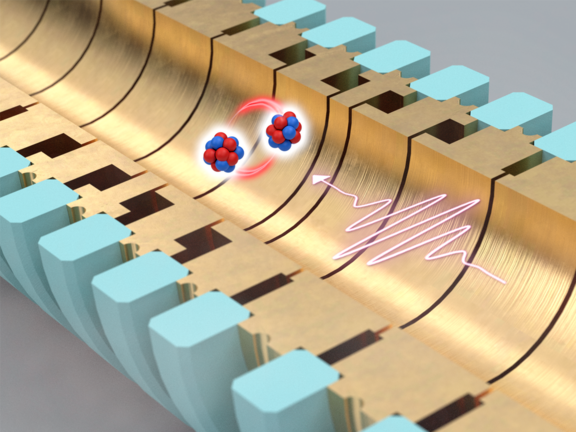
Intense laser light modifies the pairing of electrons
The quantum-mechanical exchange interaction between electrons, a consequence of the Pauli exclusion principle, can be specifically modified with…